In the world of business and personal transactions, contractual agreements are the basis of trust, accountability, and legal certainty. Whether it is the hiring of an employee, a vendor, a lease agreement for property, or the purchase of goods, contractual agreements establish the rights and responsibilities of the parties involved, especially in the context of a contractual agreement in business. It is important to have an understanding of what a contractual agreement is, the different types of contracts, and their legal implications to avoid any kind of disputes and ensure that the contract is enforceable.
This article will discuss the definition of contractual agreements, the legal aspects of contractual agreements in Indian law, the different types of contracts, and their legal implications.
What Is a Contractual Agreement?

A contract agreement is a binding promise between two or more parties that establishes enforceable rights and duties, commonly referred to as a contractual agreement between two parties. In simpler words, it is an agreement that is recognised and enforced by the law, which explains the contractual agreement meaning in practical terms.
Although the words “agreement” and “contract” are often used interchangeably, they are not the same. An agreement can only be considered a contract if it meets certain legal requirements. If not, the agreement may be valid in theory but not enforceable in a court of law.
Legal Definition Under Indian Law
According to Section 2(h) of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, a contract is defined as “an agreement enforceable by law.” This definition of a contract emphasizes the following two aspects:
- Every contract is an agreement
- Not all agreements are contracts
An agreement becomes a contract only if it fulfills the requirements set by law, and thus becomes enforceable by law.
Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
For a contractual agreement to be valid and enforceable, the following elements must be present in the agreement:
1. Offer
An offer is a specific and definite proposal made by one party to another, showing willingness to enter into a contract on certain terms.
2. Acceptance
Acceptance is the act of the other party agreeing to the offer without any conditions or alterations. Acceptance must match exactly with the terms of the offer.
3. Lawful Consideration
Consideration is something of value given in exchange between the two parties, such as money, goods, services, or a promise to do or refrain from doing something. Consideration must be lawful.
4. Capacity to Contract
The parties to a contract must possess legal capacity. This requires that they be of legal age, of sound mind, and not disqualified by law.
5. Free Consent
The consent must be free and not affected by coercion, undue influence, fraud, misrepresentation, or mistake.
6. Intention to Create Legal Relations
The parties must intend that the agreement be legally binding. Social or domestic agreement lack this intention and are therefore not enforceable.
7. Lawful Object
The object of the contract must be legal. Agreements with illegal objects are void and therefore unenforceable.
Types of Contractual Agreements
Contracts can be categorized in various ways depending on the formation, performance, and validity of the contract.
1. Types of Contracts Based on Formation
Express Contracts
Express contracts are made through the use of explicit language, either written or verbal. This is the most common type of contract.
Implied Contracts
Implied contracts are created through the actions or behavior of the parties involved. The contract is not created through written or verbal language. The intention to create a contract is inferred from the circumstances.
Quasi-Contracts
Quasi-contracts are not created by agreement but are created by law to avoid unjust enrichment. They are used to ensure fairness where one party is enriched at the expense of another.
2. Types of Contracts Based on Performance
Executed Contracts
In an executed contract, both parties have completely performed their obligations.
Executory Contracts
An executory contract is one where the obligations of one or both parties are yet to be performed.
Unilateral Contracts
In unilateral contracts, one party gives a promise in return for an act. The contract arises only after the act is performed.
Bilateral Contracts
Bilateral contracts involve mutual promises where both parties are bound to perform their respective promises.
3. Types of Contracts Based on Validity
Valid Contracts
Valid contracts are those that satisfy all the legal requirements and are fully enforceable by law.
Void Contracts
A void contract is an unenforceable contract from the start, which is either illegal or impossible.
Voidable Contracts
Voidable contracts are valid contracts that can be cancelled at the discretion of one of the parties, which is often due to the absence of free consent.
Contingent Contracts
Contingent contracts are dependent on the occurrence or absence of an uncertain future event.
Common Examples of Contractual Agreements
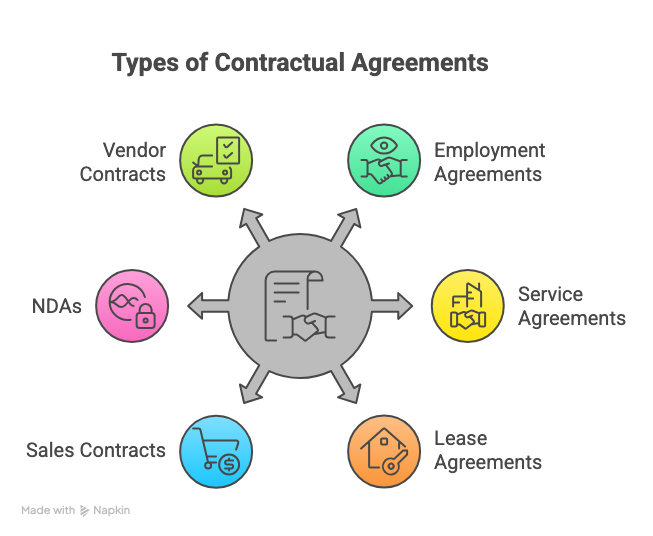
Contractual agreements are used across various personal and commercial contexts, serving as practical contractual agreement examples, including:
- Employment agreements, including a contractual agreement between employer employee
- Service and consultancy agreements
- Lease and rental agreements
- Sales and purchase contracts
- Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs)
- Vendor and supplier contracts
Legal Implications of a Contractual Agreement
Breach of Contract
Breach of contract takes place when one of the parties involved in the contractual agreement fails to fulfill their obligations. There are two types of breaches of contract:
- Minor breach of contract, which does not affect the essence of the contract
- Material breach of contract, which has a significant effect on the contract and may be a reason to terminate the contract
Remedies for Breach of Contract
In case of a breach of contract, the affected party can file a lawsuit against the other party for the following remedies:
- Damages: Compensation for the loss incurred
- Specific Performance: A court order requiring the breaching party to perform their obligations under the contract
- Rescission: Canceling the contract
- Injunction: A court order restraining a party from performing a specific act
When Is a Contract Not Enforceable?
Certain agreements are not enforceable under law, including:
- Agreements with unlawful objects or consideration
- Agreements that are vague or uncertain
- Agreements expressly declared void by law
- Agreements without consideration, unless covered by legal exceptions
Importance of Contractual Agreements in Business
Contractual agreements play a crucial role in business operations and regulatory alignment, including adherence to a contractual compliance agreement, by:
- Clearly defining rights and responsibilities
- Reducing legal and commercial risks
- Providing clarity in case of disputes
- Ensuring accountability and compliance
- Supporting structured and predictable business relationships
Conclusion
A contract is more than just a piece of paper; it is a legal binding document that regulates the relationship between the parties involved. The definition, types, and legal aspects of contracts are important to ensure that one protects his or her interests. A contract can only be effective if it is drafted in a clear manner and meets the legal requirements.
FAQs
What are the different types of contractual agreements?
The various kinds of contractual agreements are express, implied, quasi, unilateral, bilateral, executed, executory, void, voidable, and contingent contracts.
What is a contractual agreement?
A contractual agreement is a legally binding contract between two or more individuals that establishes enforceable rights and duties.
What are the five basic types of contracts?
The five basic kinds of contracts are express, implied, unilateral, bilateral, and quasi-contracts.
Why is a contractual agreement important?
A contractual agreement is significant as it establishes clear duties, safeguards legal rights, prevents disputes, and provides enforceability.



