In the modern digital-first business world, contracts are no longer confined to mere pen-written agreements around a table. Today, businesses negotiate and conclude agreements through emails, hire employees remotely, and engage in business through digital platforms such as the internet. The center on which this modern business practice revolves is electronic contracts, also referred to as E-contracts.
Electronic contracts are an important facet of modern business transactions. This ranges from clicking on ‘I Agree’ on a website to electronic contract signing in a business agreement. One must note that these are not informal agreements; rather, these are legally binding agreements that are valid under Indian law once the legal conditions are fulfilled.
Through this blog, we aim to give an overall idea of what is e contract, their process of execution, types of electronic contracts, their validity from a legal perspective in India, their benefits, and their challenges.
What Is an Electronic Contract?

The e-contract is a type of contract that is created, negotiated, and executed with the use of electronic media, while physical paper and handwritten signatures are avoided. It involves digitally creating an agreement using emails, websites, mobile applications, online forms, or electronic signature platforms, often supported by an electronic contract management system.
So, essentially, an electronic contract is no different from a conventional contract. There is a difference only with regard to the media of communication and execution of the contract.
- Electronic contracts are commonly applied in many industries:
- E-commerce and online marketplaces
- Employment and HR Onboarding
- SaaS and software licensing
- Vendor and service agreements
- Financial Services and Banking
- Freelance and consulting work
Definition of Electronic Contracts
An electronic contract can be defined as:
A contract that is created through electronic communication methods, with the parties expressing their consent through digital means without any physical interaction or written documentation.
Key Features of an Electronic Contract
1. Electronic Formation
The contract is created and communicated through the use of electronic devices like computers, smartphones, or tablets.
2. Originator and Addressee
- The originator is the party that sends or initiates the electronic contract.
- The addressee is the party that receives and accepts it.
3. Digital Consent
There are several electronic forms that consent may take, including:
- “I Agree” or “Accept” Buttons
- Entering One Time Password
- Typing a name as a signature
- Using electronic or digital signatures
- Sending an acceptance using email
4. No Physical Presence Required
There is no requirement to physically see each other in order for the contract to be valid.
How Do Electronic Contracts Work?
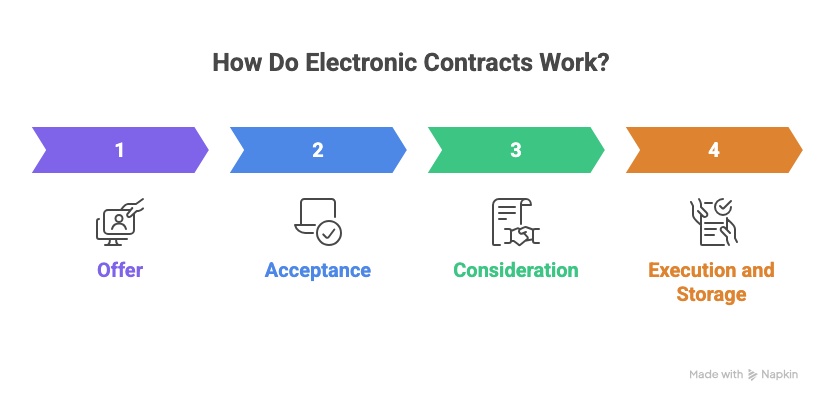
The electronic contract formation process is exactly the same as the traditional contract formation process, but technology is involved.
1. Offer
One party initiates the offer electronically using email, the internet, or an online platform.
2. Acceptance
The other party agrees to the offer digitally. The acceptance needs to be clear and unambiguous, e.g., clicking an “accept” button or sending an affirmative response by email.
3. Consideration
There must be something of value exchanged between the two parties, such as money, services, or goods.
4. Execution and Storage
In most cases, the contract, once accepted, would then be executed electronically and stored as a digital record, very often with audit trails and timestamps.
Types of Electronic Contracts
Electronic contracts may be grouped into categories based on the method used to obtain consent.
1. Click-Wrap Agreements
“Click-wrap agreements” require accepting the terms by clicking the “I Agree” or “Accept” box.
Examples:
- Software license agreements
- Online subscription sign-ups
- E-commerce checkout terms
Legal strength:
The most enforcing form of an e-contract is click-wrap agreements due to the consent involved.
2. Browse-Wrap Agreements
In a browse wrap agreement, the terms and conditions of the contract are presented on a website with a hyperlink, and the user is assumed to have agreed to the terms by continuing to use the website.
Examples:
- Website terms of use
- Privacy policies
Legal strength:
They are enforceable licenses, but this is only true if users are given due notice. Lack of clarity may impair enforceability.
3. Email Contracts
Contracts can be created through email as well, as long as there is:
- An offer, which is clear
- An clear acceptance
- Agreement upon major terms
Examples:
- Commercial negotiations concluded via email
- Vendor confirmations and service engagements
Email contracts are one of the most common these days in business transactions and are also legally valid if contractual intent is available.
Legal Validity of Electronic Contracts in India
Electronic contracts are legally binding and enforceable under Indian law, subject to the validity of contracts formed through electronic means as prescribed under existing contract and technology laws.
Governing Laws
Indian Contract Act, 1872
Electronic contracts have to fulfill all the essential elements of a valid contract, which are applicable as in any other contract.
Information Technology Act, 2000
Section 10A of the IT Act specifically states that:
The contract shall not be deemed unenforceable merely because it was formed electronically.
This provision accords electronic contracts the same legal standing as paper-based contracts, confirming the validity of electronic contracts in India.
Essential Elements of a Valid Electronic Contract
To be legally binding, an electronic contract requires:
1. Offer and Acceptance
There must be a lawful offer, as well as an acceptance through electronic media.
2. Lawful Consideration
The contract should be one in which there is an exchange of something of value.
3. Free Consent
Consent must not be obtained by coercion, fraud, misrepresentation, or undue influence.
4. Capacity of Parties
The parties to the agreement must be competent to sign the contract.
5. Lawful Object
The intention of the contract should not be illegal or prohibited by law.
Admissibility of Electronic Contracts as Evidence
In Indian Courts, electronic contracts are admissible as evidence.
According to Sections 65A and 65B of the Indian Evidence Act, electronic records can be considered valid evidence if the conditions set forth in reference to them have been satisfied.
This means:
- Emails
- Digitally signed contracts
- Online agreements
- Electronic audit logs
can all be used in legal proceedings.
Benefits of Electronic Contracts
Electronic contracting has major advantages over the traditional paper-based agreement.
1. Speed and Efficiency
Contracts can be instantly created, shared, and signed without the lengthy process brought about by printing, scanning, or courier services. This speeds up the closing of deals and business operations.
2. Cost Savings
E-contracts reduce costs related to:
- Paper and printing
- Courier and postage
- Physical storage and archiving
- Administrative handling
To organizations executing high volumes of contracts, the savings can be considerable.
3. Convenience and Accessibility
Parties can enter a contract at any time and from any place without the need to arrange a physical meeting. This is advantageous for both remote teams and international transactions.
4. Security and Traceability
The modern digital contracting platforms offer:
- Encryption
- Time-stamped signatures
- Access controls
- Detailed audit trails
These characteristics improve transparency and lower the chances of dispute related to the content.
5. Environmental Sustainability
Through the elimination of the use of paper, electronic contract use can help promote environmentally friendly business practices.
Common Challenges and Risks
Though electronic contracting has some obvious advantages, it is not without its challenges.
1. Fraud and Security Risks
If the platform is not secure, the potential risks could be:
- Identity misuse
- Forged signatures
- Unauthorized access
Using trusted and compliant platforms is essential to mitigate these risks.
2. Technical Dependence
Electronic contracts rely on:
- Internet connectivity
- Digital infrastructure
- Platform availability
Although these occurrences are unusual, they can momentarily impact execution.
3. Awareness and Compliance
Improper implementation, like lack of clear consent or record-keeping, may compromise the enforceability.
Best Practices for Using Electronic Contracts
To ensure legal validity and operational efficiency, organizations should:
- Utilize reputable and compliant e-signature tools
- Ensure the terms are clearly visible before acceptance
- Proper audit trails and electronic records
- Train teams on digital contracting process
- Complying with provisions of IT Act and Evidence Act.
Conclusion: Are Electronic Contracts the Future?
Electronic contracts have emerged as a legally valid and operationally efficient alternative to traditional contracts. And with the support of Indian legislation, they also provide the added bonus of speed, savings, convenience, and security, making them a necessity in business today.
As businesses are increasingly adopting digital workflows, electronic contracts can no longer be considered optional; they have to be considered the foundation of efficient legal operation and scalable businesses.



